 Your cornea helps your eyes see clearly by focusing incoming light on your retina. The top eye specialists at Austin Eye discuss what you need to know about your cornea to keep your eyes healthy.
Your cornea helps your eyes see clearly by focusing incoming light on your retina. The top eye specialists at Austin Eye discuss what you need to know about your cornea to keep your eyes healthy.
Your Cornea
The clear layer in front of your pupil and iris is the cornea. Unlike most bodily tissues, it does not receive nourishment from blood cells. Instead, tears nourish the cornea, along with the aqueous humor. That is the clear fluid between the cornea and the vitreous.
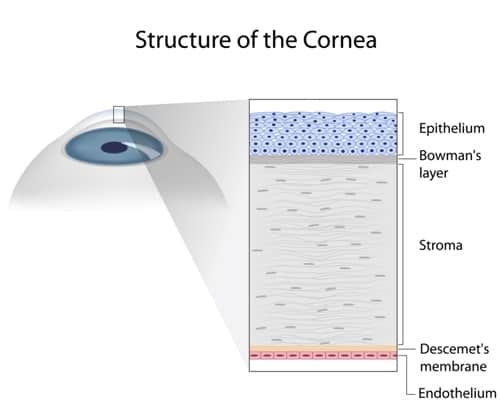
The cornea serves as the outermost lens of the eye. It also protects the eye from infections. There are five layers to the cornea:
- Epithelium – The outermost layer, which protects the eyes by blocking dust, bacteria and foreign materials.
- Bowman’s layer – Beneath the epithelium, this layer consists of collagen, a type of protein fibers. If damaged, the ensuing scarring may cause vision loss.
- Stroma – Comprising the bulk of the cornea, this layer consists primarily of water and collagen.
- Descemet’s membrane – This thin but strong piece of tissue serves as a barrier against injuries and infection.
- Endothelium – A very thin layer, the endothelium works to keep the cornea clear. Its most important function is drawing excess fluid away from the stroma. Otherwise, the stroma would become swollen with water, causing haziness and impenetrability to light.
Corneal Disorders
Corneal disorders may result in loss of visual acuity, or sharpness. Pain is the primary symptom of a corneal disorder, and so is tearing. While allergies or injuries may harm the cornea, other common corneal disorders include:
- Corneal dystrophies – The buildup of material on the cornea causing vision clouding. Corneal dystrophies are often hereditary and usually quite painful.
- Corneal ulcers – Also known as keratitis, this condition involves an open sore on the eye. Without prompt treatment, vision loss may occur.
- Dry eye – Lack of sufficient tear production or an imbalance in the tear film causes discomfort and vision issues.
- Interstitial keratitis – This serious disorder generally occurs after an eye infection. Inflammation affects the cornea’s middle layers.
- Keratoconus – This disorder causes thinning and bulging of the middle part of the cornea. Swelling and eventual scarring may result, along with slow dimming of sight. Correction may require corneal transplant surgery.
- Superficial punctuate keratitis – The death of small groups of cells on the corneal surface may cause this condition. Along with tearing and redness, symptoms include light sensitivity and decreased vision.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for corneal disorders include:
- Contact lens wear
- Eye abrasions
- Eyelid disorders
Caring for Your Cornea
Help maintain good corneal health by consuming a diet full of fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts and fatty fish such as salmon. Your eye doctor can recommend a vitamin and mineral supplement that can aid in protecting your cornea.
Regular exercise benefits your body in many ways, and that includes eye health. Smoking is harmful to virtually every part of the body, and the eyes are no exception.
Contact Us
If you experience any symptoms of corneal disease or would like additional information about the function of your cornea, contact the dedicated eye care specialists at Austin Eye to schedule a consultation.







